This article aims to educate readers on the fragility of our power and infrastructure grid and underscore our reliance on these systems. It will address the grid’s vulnerabilities and emphasize the significance of preparation, planning, and training. Informed decisions are facilitated by the comprehensive collection of information. At Gen Six Solutions, we spotlight issues and concentrate on devising solutions. Below are some identified problems.
Since 2008, the number of reported attacks on the country’s power grid has nearly doubled annually. For clarity, I categorize critical infrastructure with the power grid due to its importance and susceptibility. Most citizens, not having experienced extended power outages, fail to recognize the fragility and vulnerability of our nation’s grid. The era when only storms threatened our grid has passed. Currently, with malicious actors and their cyberattack capabilities, there are no physical security barriers protecting our power substations from physical attacks.
Physical Attacks:
During the first quarter of 2024, national utility companies reported more than 60 incidents classified as physical threats or attacks on critical grid infrastructure. This figure represents a doubling from the same period in the previous year. Notably, these physical attacks often involved the use of firearms. Such attacks, which are both easy to orchestrate and low-cost, have caused and continue to pose significant damage.
In 2022, tens of thousands were left without power in North Carolina in what the FBI described as an “intentional and targeted” act. It is also noteworthy that this area in North Carolina houses many active duty Special Forces soldiers stationed at the nearby Fort Liberty (formerly known as Fort Bragg).
Communication Gaps:
Despite escalating threats, gaps in communication persist between law enforcement and state/federal regulators. The absence of preventive measures and risk mitigation leaves many officials and policymakers apparently oblivious to the full scope of dangers posed by power outages and cyberattacks. In April 2024, states including Texas, South Dakota, Nevada, and Nebraska experienced disruptions in their emergency communication and dispatch platforms. This led to numerous problems, such as unanswered calls and hospital transportation delays. Texas authorities attributed the situation to an accidentally severed fiber optic cable. Although the cause of the outage was not confirmed, the provided explanation is concerning. The severance of a single cable causing such widespread disruption across vast, separate states in the west is alarming and warrants concern.
Cybersecurity Concerns:
The National Intelligence Agency reports that the U.S. and Canadian power grid has been targeted in over 1,600 attacks. The expansive U.S. grid, comprising approximately 7,300 power plants, 55,000 transmission substations, and 160,000 miles of high-voltage lines, is a prime target. It operates on a vast, interconnected network managed by Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, which are known to be particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks. This vulnerability was notably exploited in the Stuxnet attacks on Iranian nuclear facilities. Such attacks can be readily executed by malicious entities, cybercriminals, and extremist groups.
Common SCADA Vulnerabilities:
Connectivity to the Public Internet: When SCADA systems are directly accessible from the internet, they become vulnerable to attacks. Isolating them from public networks is crucial.
Unpatched Legacy Software: Outdated operating systems (e.g., Windows XP and 2000) can harbor security flaws. Regular patching and updates are essential.
Weak Authentication: Weak or default credentials can be exploited by attackers. Strong authentication mechanisms are vital.
Lack of Antivirus Software: Without proper protection, SCADA systems are susceptible to malware.
Rogue Devices: Unauthorized or unrecognized devices connected to the network pose risks.
Undetected Malware and APTs: Persistent threats can infiltrate SCADA systems undetected12.
Sectors and Infrastructures with SCADA Systems:
Smart buildings
Smart cities and transportation networks
Oil and gas facilities
Energy generation and distribution plants
Wastewater treatment and distribution
Manufacturing industries
Food production facilities
With all of these threats seemingly closer than ever, what can be done to prepare?
Solution #1 Identify power needs
Many people are uncertain about where to begin with electricity and alternative power sources in the event of a grid failure. The initial step should be to identify the essential appliances and devices for your household. Once you determine the wattage requirements to sustain a degree of normality during an emergency, the process of shopping for and understanding the necessary power or wattage becomes simpler. The following is an example of a wattage usage chart.
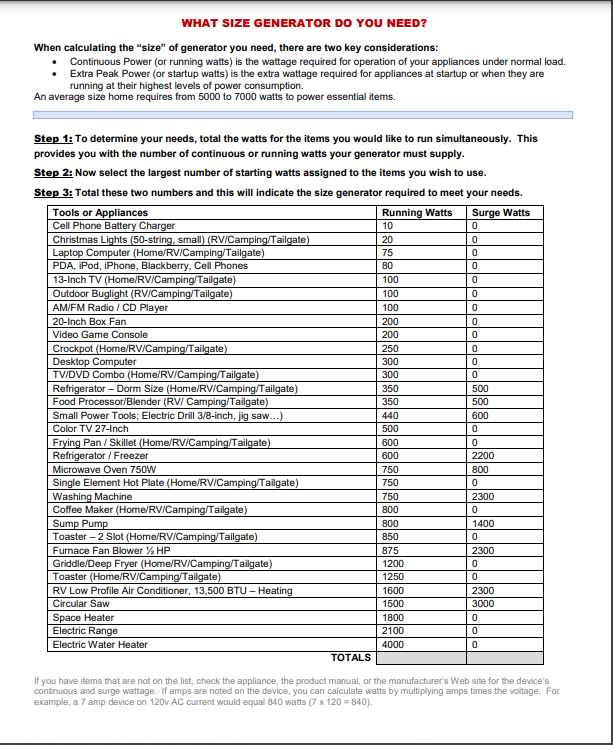
Solution #2: Come up with lines of effort according to COA’s
When analyzing and preparing for potential threats, it is always best to practice identifying the threats and developing specific COA’s (courses of action) to respond to that threat. While it may seem overwhelming at first, remember practice makes perfection. I recommend starting with most dangerous/deadly first (MDCOA) and working backwards to address the most likely (MLCOA) along with triggering events. For example, If XX happens, that we do YYYY. This task can be analyst heavy and requires careful planning and training to smooth out wrinkles. Of course, if necessary, reach out to Gen Six Solutions for assistance in developing a customized action plan.
Solution #3: Identify SIP or GOT triggers and pace plans.
SIP and GOT stand for shelter in place and get out of town. We recommend developing PACE (primary, alternate, contingency, emergency) power plans for each scenario. Also talk with family and friends with what triggering events are and how the events dictate your reaction options. This may seem like a common sense step, but the fog of confusion can have devastating affects if plans aren’t clearly stated.
Contact Gen Six Solution at info@gensixsolutions to schedule a consultation and visit our affiliate links to aid in your preparedness journey.
